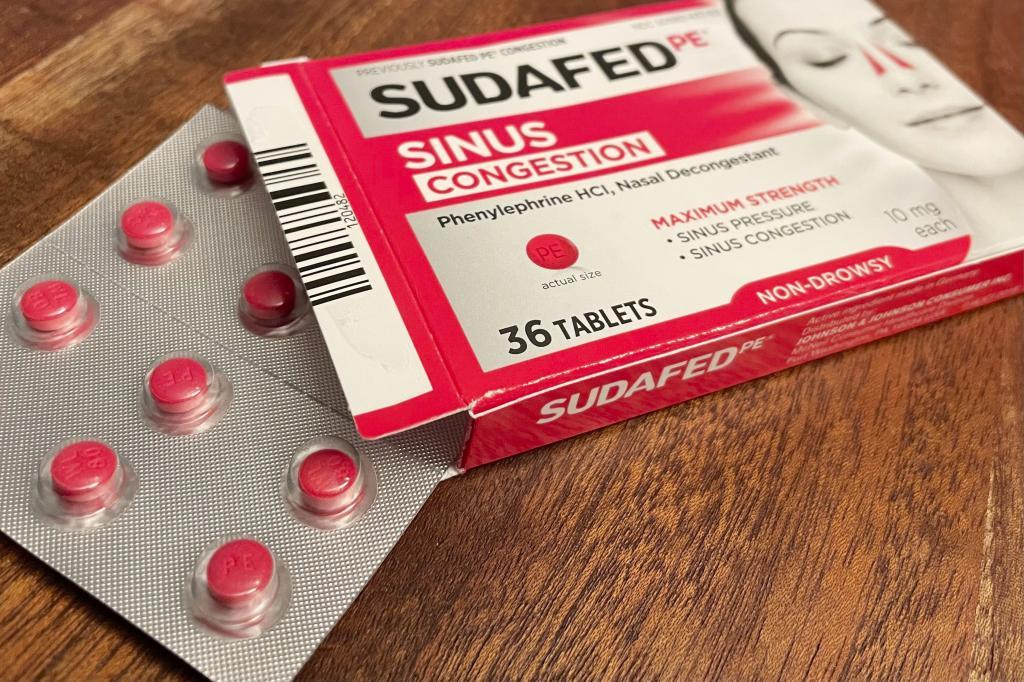
Changes are coming to the cold and cough aisle of your local pharmacy: U.S. officials are moving to phase out the leading decongestant found in hundreds of over-the-counter medicines, concluding that it doesn't actually relieve nasal congestion.
Phenylephrine is used in popular versions of Sudafed, Dayquil and other medications, but experts have long questioned its effectiveness. Last month the Food and Drug Administration formally proposed revoking its use in pills and liquid solutions, kicking off a process that's likely to force drugmakers to remove or reformulate products.
It's a win for skeptical academics, including researchers at the University of Florida who petitioned the FDA to revisit the drug's use in 2007 and again in 2015. For consumers it will likely mean switching to alternatives, including an older decongestant that was moved behind the pharmacy counter nearly 20 years ago.
Doctors say Americans will be better off without phenylephrine, which is often combined with other medicines to treat cold, flu, fever and allergies.
"People walk into the drugstore today and see 55,000 medicines on the shelf and they pick one that is definitely not going to work," said Dr. Brian Schroer of the Cleveland Clinic. "You take away that option and it will be easier for them to self-direct toward products that really will help them."
The FDA decision was expected after federal advisers last year voted unanimously that oral phenylephrine medications haven't been shown to relieve congestion.
Experts reviewed several recent, large studies indicating that phenylephrine was no better than a placebo at clearing nasal passageways. They also revisited studies from the 1960s and 1970s that supported the drug's initial use, finding numerous flaws and questionable data.
The panel's opinion only applied to phenylephrine in oral medications, which account for roughly $1.8 billion in annual U.S. sales. The drug is still considered effective in nasal sprays, though those are much less popular.
Phenylephrine wasn't always the top choice for cold and allergy products. Many were originally formulated with a different drug, pseudoephedrine.
But a 2006 law required pharmacies to move pseudoephedrine products behind the counter, citing their potential to be processed into methamphetamine. Companies such as Johnson & Johnson and Bayer decided to reformulate their products to keep them readily available on store shelves — and labeled many of them as "PE" versions of familiar brand names.
Consumers who still want to take pills or syrups for relief will probably need to head to the pharmacy counter — where the pseudoephedrine-containing versions of Sudafed, Claritin D and other products remain available without a prescription. Purchasers need to provide a photo ID.
Beyond those products, most of the other options are over-the-counter nasal sprays or solutions.
Saline drops and rinses are a quick way to clear mucus from the nose. For long-term relief from seasonal stuffiness, itching and sneezing, many doctors recommend nasal steroids, sold as Flonase, Nasacort and Rhinocort.
"These medicines are by far the most effective daily treatment for nasal congestion and stuffiness," Schroer said. "The biggest issue is they're not great when used on an as-needed basis."
Nasal steroids generally have to be used daily to be highly effective. For short-term relief, patients can try antihistamine sprays, such as Astepro, which are faster acting.
Phenylephrine-based sprays will also remain on pharmacy shelves.
The experts who challenged the drug's effectiveness say it's quickly broken down and rendered ineffective when it hits the stomach.
"This is a good drug, but not when it's swallowed," said Leslie Hendeles, professor emeritus at the University of Florida's College of Pharmacy, where he co-authored several papers on the ingredient. "It's inactivated in the gut and doesn't get into the bloodstream, so it can't get to the nose."
When Hendeles and his colleagues first petitioned the FDA on phenylephrine, they suggested a higher dose might be effective. But subsequent studies showed that even doses 400% higher than those currently recommended don't treat stuffiness.
The FDA and other researchers concluded that pushing the dosage even higher might carry safety risks.
"If you're using very high doses, the risk is raising blood pressure so high that it could be hazardous to patients," said Randy Hatton, a University of Florida professor who co-led the research on phenylephrine.
Because of its cardiovascular effects, the drug is sometimes used to treat dangerously low blood pressure during surgery, Hatton noted.
Oral phenylephrine medicines will still be with us for a while.
Government regulators must follow a public, multistep process to remove the ingredient from FDA's list of drugs approved for over-the-counter decongestants.
For six months, the FDA must take comments on its proposal, including from consumers and companies. Then, the FDA must review the feedback before writing a final order. Even after that decision is finalized, companies will likely have a year or more to remove or reformulate products.
Drugmakers could further delay the process by requesting additional FDA hearings.
For now, the Consumer Healthcare Products Association — which represents medicine makers — wants the products to stay available, saying Americans deserve "the option to choose the products they prefer for self-care."
Hatton says he and his colleagues disagree: "Our position is that choosing from something that doesn't work isn't really a choice."